面向对象模型
成员变量和函数的存储
C++ 实现了 “封装”,数据和处理数据的操作是分开存储的。 C++ 中非静态数据成员直接内含在类对象中,成员函数虽然内含在 class 声明之内,却不出现在对象中。每一个非内联成员函数只会诞生一份函数实例。 也就是说成员函数和静态成员一样,是类的所有对象共享的。
sizeof(Data1) 的大小只是类的对象所占的空间大小。
this 指针
this 指针工作原理
通过上个例子我们知道,C++的数据和操作是分开存储的,并且每一个非内联函数只会诞生一份函数实例,也就是说多个同类型的对象会共用一块代码,那么问题是:这一块代码是如何区分是哪个对象调用的自己呢?
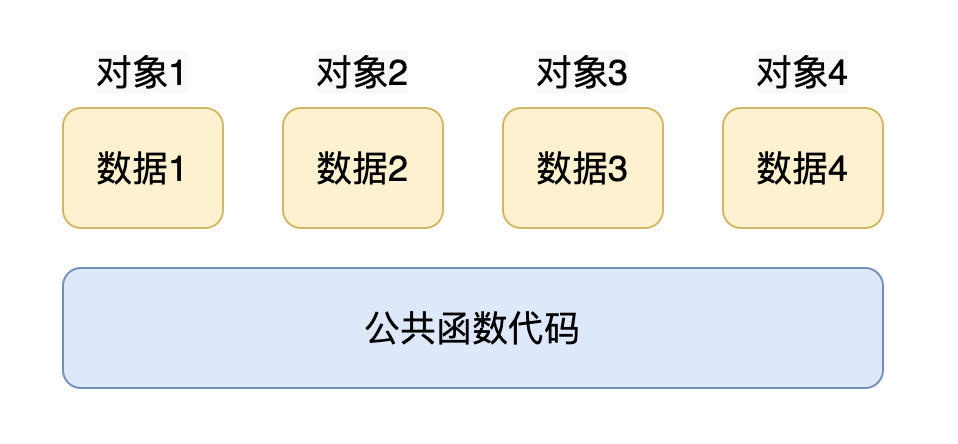
答案就是:通过 this 指针。 C++ 通过提供特殊的对象指针,this 指针,解决了上述问题。this 指针指向被调用的成员函数所属的对象。
成员函数通过 this 指针即可知道操作的是哪个对象的数据。 This 指针是一种隐含指针,它隐含于每个类的非静态成员函数中。This 指针无需定义直接使用即可。
public:
int mA;
void setA(int a)
{
mA = a;
// this-> 可写可不写,编辑器会自动帮我们添加
this->mA = a;
}
注意:静态成员函数没有this指针,静态成员函数不能操作非静态成员变量。
this 指针的应用
1、函数形参和成员同名可以使用this指针
class Data1
{
public:
int a;
public:
// 函数的形参和成员变量同名,可以用this指针区分
Data1(int a)
{
cout << this << endl;
}
};
void test01()
{
Data ob1(10);
cout << ob1.a << endl;
cout << &ob1 << endl;
}
2、this 来完成链式操作
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Data1
{
public:
Data1& myPrintf(char *str)
{
cout << str << " ";
return *this;
}
};
void test01()
{
// 套娃操作
Data1().myPrintf("hello").myPrintf("world");
}
const修饰成员函数
用 const 修饰成员函数的时候, const 修饰 this 指针指向的内存区域,成员函数体内不可以修改本类中的任何普通成员变量,当成员变量类型前用 mutable 修饰的时候除外。
class Data
{
public:
int a;
int b;
mutable int c;
public:
Data(int a, int b, int c)
{
this->a = a;
this->b = b;
this->c = c;
}
// const 修饰成员函数为只读(该成员函数不允许对成员函数赋值)
// mutable 修饰的成员除外
void showData(void) const
{
c = 100;
cout << a << " " << c << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
Data ob1(10, 20, 30);
ob1.showData();
}
友元
类的主要特点之一是数据隐藏,即类的私有成员无法在类外访问,但是有时候需要再类外部访问类内部的私有成员,怎么办?
解决方法是使用友元函数,友元函数是一种特权函数,C++允许这个特权函数访问私有成员。
友元的语法
使用 friend 关键词声明友元
friend 关键词只出现在声明处,一个函数或者类作为了另一个类的友元,那么这个函数或类就可以直接访问 另一个类的私有数据。
普通全局函数作为类友元
在类的内部声明一个全局函数为友元,这个全局函数就可以访问类的私有成员。 下面就是一个普通全局函数作为类友元的例子。
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Room
{
// 全局函数作为类的友元
friend void visiting01(Room &room);
private:
string bedroom;
public:
string setingroom;
public:
Room(string bedroom, string setingroom)
{
this->bedroom = bedroom;
this->setingroom = setingroom;
}
};
// 普通全局函数
void visiting01(Room &room)
{
cout << room.bedroom << endl;
cout << room.setingroom << endl;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
Room room("卧室", "客厅");
visiting01(room);
return 0;
}
类的某个成员函数 作为另一个类的友元
class Room; // 向前声明,只说明类名称
class goodGay
{
public:
void visiting01(Room &room);
void visiting02(Room &room);
};
class Room
{
friend void goodGay::visiting01(Room &room);
private:
string bedroom;
public:
string setingroom;
public:
Room(string bedroom, string setingroom)
{
this->bedroom = bedroom;
this->setingroom = setingroom;
}
};
void goodGay::visiting01(Room &room)
{
cout << room.setingroom << endl;
}
void goodGay::visiting02(Room &room)
{
cout << room.bedroom << endl;
cout << room.setingroom << endl;
}
int main()
{
Room room("卧室", "客厅");
goodGay gg;
gg.visiting01(room);
gg.visiting02(room);
}
友元的注意事项
1、友元关系不能被继承
2、友元关系是单向的,类A是类B的朋友,但类B不一定是类A的朋友
3、友元关系并不具有传递性
友元案例(遥控器的类)
编写一个电视机类,电视机具有关机和开机的状态,有音量操作的方法、频道操作的方法。由于电视机只能逐一调整频道,不能指定频道,增加遥控器类,遥控器类除了拥有电视机已有的功能,再增加更具输入调台的功能。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class TV;
// 遥控器的类作为TV的友元
class Remote
{
private:
TV *p;
public:
Remote(TV *p);
void offOrOn();
void offOrOn(void);
void upVolume(void);
void downVolume(void);
void upChannel(void);
void downChannel(void);
void setChannel(int channel);
};
class TV
{
friend class Remote;
enum{OFF, ON};
enum{minVol, maxVol=10};
enum{minChan, maxChan=25}
private:
int state;
int volume;
int channel;
public:
TV()
{
state = OFF;
volume = minVol;
channel = minChan;
}
void offOrOn(void);
void upVolume(void);
void downVolume(void);
void upChannel(void);
void downChannel(void);
void showTV(void);
};
int main()
{
TV tv;
auto re = Remote(&tv);
re.offOrOn();
re.setChannel(10);
re.upVolume();
return 0;
}
void TV:offOrOn()
{
state = (state == ON) ? OFF : ON;
}
void TV::upVolume()
{
if(volume == maxVol)
{
volume = maxVol;
}
else
{
volume++;
}
}
void TV::downVolume()
{
if(volume == minVol)
{
volume = minVol;
}
else
{
volume--;
}
}
void TV::upChannel()
{
if(channel == maxChan)
{
channel = minChan;
}
else
{
channel++;
}
}
void TV::downChannel()
{
if(channel == minChan)
{
channel = maxChan;
}
else
{
channel--;
}
}
void TV::showTV()
{
cout << "电视机的状态:" << state << endl;
cout << "电视机的音量:" << volume << endl;
cout << "电视机的频道:" << channel << endl;
}
void Remote::offOrOn()
{
p->offOrOn();
}
void Remote::upVolume()
{
p->upVolume();
}
void Remote::downVolume()
{
p->downVolume();
}
void Remote::upChannel()
{
p->upChannel();
}
void Remote::downChannel()
{
p->downChannel();
}
void Remote::setChannel(int channel)
{
if(channel < p->minChan || channel > p->maxChan)
{
cout << "频道设置错误" << endl;
}
else
{
p->channel = channel;
}
}